
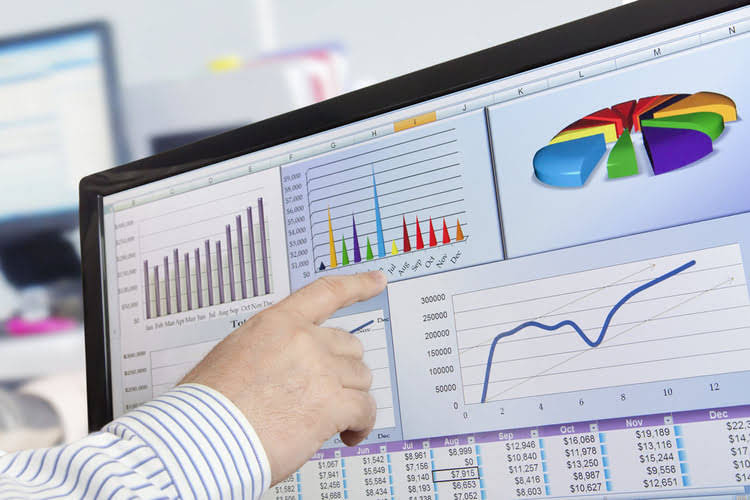
In this article, we will discuss the formula for predetermined overhead rate and how to calculate it. The overhead cost per unit from Figure 6.4 is combined with the direct material and direct labor costs as shown in Figure 6.3 to compute the total cost per unit as shown in Figure 6.5. The equation for the overhead rate is overhead (or indirect) costs divided by direct costs or whatever you’re measuring. Direct costs typically are direct labor, direct machine costs, or direct material costs—all expressed in dollar amounts. Each one of these is also known as an “activity driver” or “allocation measure.”
How to calculate the present value of a perpetuity for business valuation

Both of these scenarios can have a significant impact on a company’s financial statements, and it is important to address them promptly. This includes keeping track of the actual overhead costs incurred and the activity levels during the period. Accurate record keeping can help to ensure that the POHR is calculated accurately and that the overhead costs are allocated correctly. For example, the total direct labor hours estimated for the solo product is 350,000 direct labor hours. With $2.00 of overhead per direct hour, the Solo product is estimated to have $700,000 of overhead applied. When the $700,000 of overhead applied is divided by the estimated production of 140,000 units of the Solo product, the estimated overhead per product for the Solo product is $5.00 per unit.
- Therefore, they use labor hours for the apportionment of their manufacturing cost.
- Using a predetermined rate, companies can assign overhead costs to production when they assign direct materials and direct labor costs.
- The manufacturing overhead costs are applied to the product based on the actual number of activity base units used during the accounting period.
- For example, if a company produces a product that requires a lot of labor, then the POHR will be higher than if the product requires less labor.
- As mentioned in the prior example for flat perpetuity, the $1,000 annual payment is kept constant throughout the entire duration of the investment.
- According to a survey 34% of the manufacturing businesses use a single plant wide overhead rate, 44% use multiple overhead rates and rest of the companies use activity based costing (ABC) system.
Ethical Cost Modeling
The overhead rate is a QuickBooks cost allocated to the production of a product or service. Overhead costs are expenses that are not directly tied to production such as the cost of the corporate office. To allocate overhead costs, an overhead rate is applied to the direct costs tied to production by spreading or allocating the overhead costs based on specific measures.
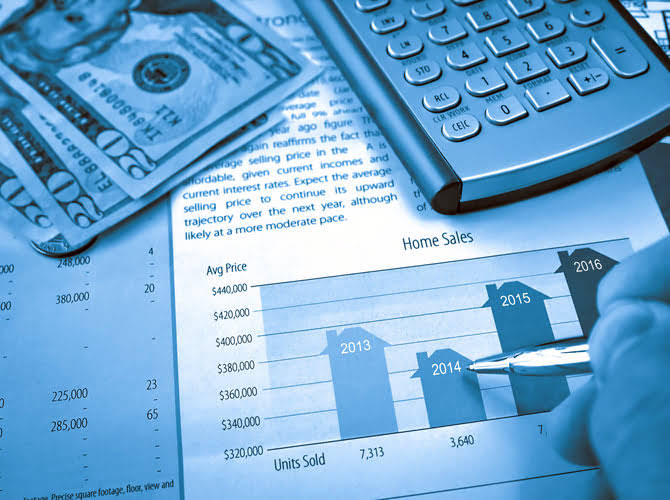

Monitoring relative expenses
For example, a production facility that is fairly labor intensive would likely determine that the more labor hours worked, the higher the overhead will be. As a result, management would likely view labor hours as the activity base when applying overhead costs. For example, let’s assume that a company estimated its overhead costs to be $100,000 for the year and allocated this amount to its products using a predetermined overhead rate of $10 per unit. Bakery Accounting If the company produced and sold 10,000 units during the year, the underapplied overhead of $20,000 would be added to the cost of goods sold, resulting in an increase of $2 per unit. This means that the cost of each unit sold would be $12 instead of $10, reducing the gross profit margin and the net income.
- Again, this predetermined overhead rate can also be used to help the business owner estimate their margin on a product.
- It ensures that overhead costs are allocated correctly to products or services and allows organizations to set competitive prices while also making a profit.
- The formula for a predetermined overhead rate is expressed as a ratio of the estimated amount of manufacturing overhead to be incurred in a period to the estimated activity base for the period.
- Thus, the implications of overhead allocation are far-reaching within a business context.
- Plus, the information can be used in pricing decisions and profitability analysis of each product.
- It’s an integral part of financial decision-making, pricing strategy, and profitability analysis of a company.
What Is a Predetermined Overhead Rate?
Underapplied overhead occurs when the actual overhead costs incurred by a company are more than the estimated overhead costs used to calculate the predetermined overhead rate POR. This means that the company has allocated less overhead costs to its products or services than it should have, resulting in an understatement of the total cost of production. Underapplied overhead is a significant issue for companies as it can affect their profitability and financial reporting. These overhead costs involve the manufacturing of a product such as facility utilities, facility maintenance, equipment, supplies, and labor costs. Whereas, the activity base used for the predetermined overhead rate calculation is usually machine hours, direct labor hours, or direct labor costs. Albert Shoes Company calculates its predetermined overhead rate on the basis of annual direct labor hours.

Example of a Predetermined Overhead Rate
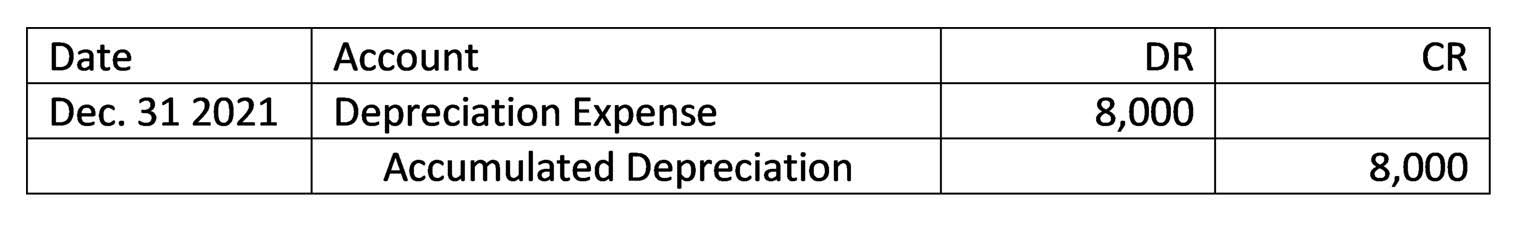
By failing to assigncosts to all of the activities, touring bicycles were subsidizingmountain bicycles. Activity-based costing has revealed that low-volume,specialized products have been the cause of greater costs thanmanagers had realized. Now management can estimate how much overhead will be required for upcoming work or even competitive bids. For instance, assume the company is bidding on a job that will most likely take $5,000 of labor costs. The management can estimate its overhead costs to be $7,500 and include them in the total bid price.